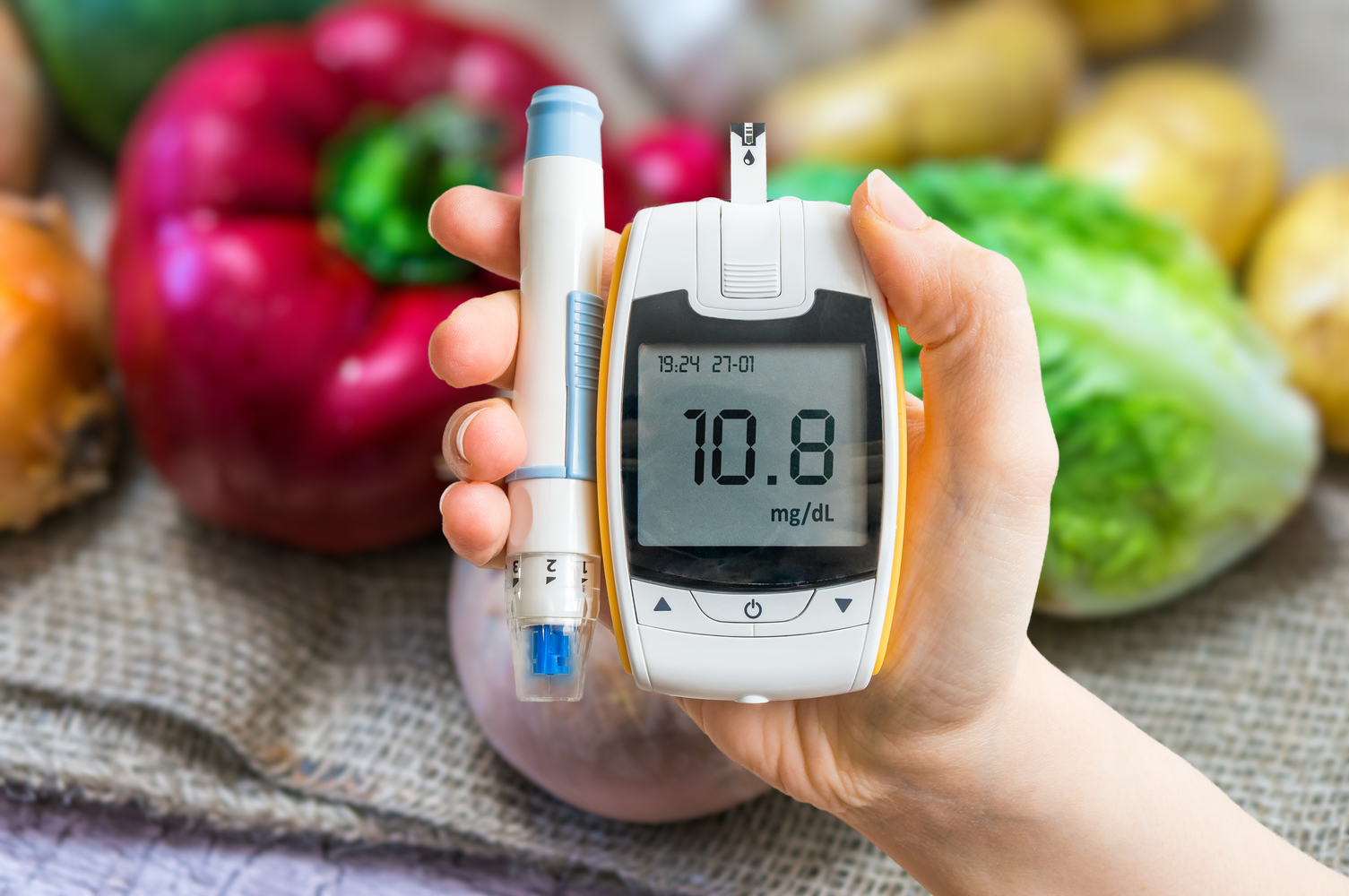
Oral and Intravenous Medicines for Diabetes
It is not a herculean task to keep diabetes under control. A disciplined approach to this condition will help you keep the blood sugar at a stable level. There are different treatments for diabetes that not only include medications, but also unconventional approaches without medications. These include home remedies and changes in lifestyle, such as a healthy diet and physical activity.
However, some of the common medicine for diabetes include pills and intravenous medicines. The often-used treatments for diabetes are listed below.
1. Medications
The oral medications to treat diabetes can be divided into different categories. They can include:
- Metformin
It is an oral antidiabetic agent and the first line of treatment for managing type-2 diabetes (non-insulin dependent). Metformin is available in the market under different brand names like Glucophage, Glumetza, Fortamet, among others. It is the most commonly used medication when diabetes is not diet controlled. It lowers glucose production in the liver and helps the body to use insulin effectively. - Sulfonylureas
It helps the pancreas to secrete more insulin. The most commonly used medicines are glipizide, glyburide, and glimepiride. - Meglitinides
It also stimulates the pancreas to produce more insulin, and medicines like Starlix and Prandin belong to this category. - Thiazolidinediones
Actos and Avandia are some medicines used, but they are not the first-line treatment in diabetes as they are linked to weight gain. They are usually used as second or third-line treatments. - DPP-4 Inhibitors – Januvia, Onglyza, and Tradjenta
These medicines help decrease blood sugar levels. Compared to other classes of medicines, they do not cause weight gain as a side effect but may contribute to joint pain. - GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
These medicines slow the process of digestion and in turn reduce the blood glucose levels. Some examples of this medicine include Byetta and Victoza. - SGLT2 Inhibitors
These help in preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing sugar into the blood and help excrete the sugar in the urine. Drugs like Invokana and Jardiance are some commonly-used SGLT2 inhibitors.
2. Injections
Insulin is the most commonly used injectable for the treatment of diabetes. There are different types of insulin injections such as rapid-acting, regular, intermediate-acting, and long-acting insulins. Some of the insulins used are:
- Humalog and Novolog are rapid-acting insulin and take effect at the same time the meal is taken or within 15-30 minutes, but the insulin needs are met only for a short period.
- Lantus and Levemir are long-acting insulin. They take around 1-4 hours for the onset of action but last up to 24 hours.
- Regular Insulin or short-acting insulin requires 30 minutes to 1 hour to reach the bloodstream but lasts for 12 hours to meet the insulin requirements of the body.
- NPH or intermediate-acting insulin requires one and a half hours to 4 hours to take effect but lasts for up to 24 hours in the body.
3. Insulin Pump Therapy
It is a widely used therapy for the treatment of diabetes and involves providing both basal insulin and bolus insulin.
- Basal insulin
The insulin pump has a certain basal insulin dose set and provides it in small amounts throughout the day. - Bolus insulin
It is usually given as a single large bolus, especially when a person has high blood glucose or before a heavy carbohydrate meal.